- 1. Goals
- 2. Workflow Overview
- 3. The Use case for this Lab
- 4. Configure your environment and core services
- 5. Let’s build our services
- 5.1. Setup Wildfly-Swarm plugins
- 5.2. Create The BookService Project in Forge
- 5.3. Create The BookService Frontend Project in Forge
- 5.4. Create The SellingPoint service Project in Forge
- 5.5. Add geospatial endpoint in SellingPoint
- 5.6. Update Frontend App to consume the new SellingPoint Service
- 5.7. Secure the endpoints with KeyCloak
- 5.8. Enable Application Performance Monitoring
- 5.9. Putting it all together
- 5.10. Bootstrap data
- 6. Extend the Demo with more capabilities
1. Goals
-
Understand where to start when building microservices
-
Get up and running deploying
microservicesonWildfly-SwarmwithForge. -
Build a microservices based application using incremental steps to add capabilities along the way.
-
Secure your application endpoints using
Keycloak -
Manage your application performance with
Hawkular -
Build
polyglot microservicesby replacing some of the services with their equivalent inNode.jsandVert.X -
Explore different deployment options of your
microserviceswithDockerandOpenshift
2. Workflow Overview
While a microservices architecture doesn’t mandate using a specific language for implementation we decided here to take a pragmatic approach, we will choose the Java EE path with Wildfly-Swarm, then later in our demo, once we completed our basic app, we will explore how these services can interact with other services that may be implemented using a different technology such as Spring Boot, Vert.X, Node.JS etc…
But let’s keep that for the last section.
3. The Use case for this Lab
-
Create a bookstore app with Forge that contains :
-
A book/Author model (title / author name)
-
A SellingPoint Object containing location info (latitude / longitude)
-
This part with be extracted later as a swarm service
-
-
-
Scaffold AngularJS front end for this app
-
Initially deploy this app as an "old school" WAR on WF
-
"explode" the app into 3 different swarm apps :
-
A book/author service
-
A Selling point service
-
A front end (an "empty" swarm app containing just a web-app folder, ideally this should be a standalone webapp running nodejs, but is a bit out of scope for JavaOne audience)
-
-
"secure" the 3 swarm apps with KeyCloak
-
Here we introduce a 4th swarm app with the KeyCloak server
-
-
Add Hibernate Search fraction to the Selling Point service and show geospatial queries
-
Bonus point could be showing HB Search integration with Elastic Search
4. Configure your environment and core services
In this section we will be following the steps as defined in the Overview section. The steps can be followed an executed as individual pieces or you can run the full Forge script script available here.
4.1. Setup Core Services
4.1.1. Security - Keycloak
In this session we will be using the purposely build Keycloak Wildfly-Swarm uberjar.
4.1.2. Application Performance Management - Hawkular
We will be using the application performance management, distributed tracing and Business Transaction Management capabilities that are available with Hawkulat APM
To install, download and unpack the Hawkular APM distribution. The distribution includes both the server and the agent.
Create an application user with "read-write,read-only" roles.
Once user is created, start the server with a port offset to avoid conflict with the other services:
$APM/bin/standalone.sh -Djboss.socket.binding.port-offset=100Then before running any of the services, in the command shell run:
. $APM/apm/setenv.sh <port> (e.g. 8180)Once you have build the services later in this lab, run the service with $JAVA_OPTS supplied:
java $JAVA_OPTS -jar ./target/mylab-swarm.jar5. Let’s build our services
5.1. Setup Wildfly-Swarm plugins
addon-install-from-git --url https://github.com/forge/wildfly-swarm-addon.git
addon-install-from-git --url https://github.com/forge/keycloak-addon.git5.2. Create The BookService Project in Forge
# create the BookService project
# ---------------- Book Service [:8080/rest] ---------------
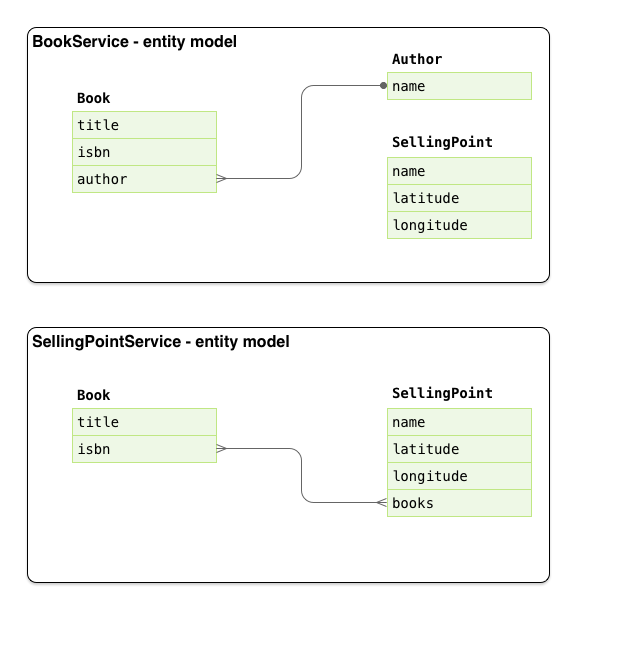
project-new --named bookservice --stack JAVA_EE_7
# create Author entity
jpa-new-entity --named Author
jpa-new-field --named name
# create Book entity and relationship with Author
jpa-new-entity --named Book
jpa-new-field --named title
jpa-new-field --named isbn
jpa-new-field --named author --type org.bookservice.model.Author --relationship-type Many-to-One
# create SellingPoint entity
jpa-new-entity --named SellingPoint
jpa-new-field --named name
jpa-new-field --named latitude --type Double
jpa-new-field --named longitude --type Double
# scaffold and create endpoints
scaffold-generate --provider AngularJS --generate-rest-resources --targets org.bookservice.model.*
# At this stage you can build and deploy a regular JAR
# and deploy to a Java EE7 compliant server like EAP 7 and Wildfly 10
# Since this lab is about Wildfly-Swam let's swarmify this
# Unless you which more control and create your own Main class,
# No change in your code is needed. Only Maven coordinate requires updating.
wildfly-swarm-setup
wildfly-swarm-detect-fractions --depend --build
# enable CORS
rest-new-cross-origin-resource-sharing-filter5.3. Create The BookService Frontend Project in Forge
# ---------------- Book Store Web Front End [:8081/rest] ---------------
# Now we want to create front end swarm service to access BookService
project-new --named bookstorefrontend --stack JAVA_EE_7 --type wildfly-swarm --http-port 8081
wildfly-swarm-add-fraction --fractions undertow
mv ../bookservice/src/main/webapp/ src/main/
# Keep empty src/main/webapp/WEB-INF
mkdir ../bookservice/src/main/webapp
mkdir ../bookservice/src/main/webapp/WEB-INF
# change the url in the angular services to point
# to http://localhost:8080/rest/ in src/main/webapp/scripts/services
cp ../frontend_assets/services/AuthorFactory.js src/main/webapp/scripts/services/
cp ../frontend_assets/services/BookFactory.js src/main/webapp/scripts/services/5.4. Create The SellingPoint service Project in Forge
# ---------------- SellingPoint Service [:8082/rest] ---------------
# create SellingPoint service
project-new --named sellingPoint --stack JAVA_EE_7 --type wildfly-swarm --http-port 8082
wildfly-swarm-add-fraction --fractions hibernate-search
# create Book entity and relationship with Author
jpa-new-entity --named Book
jpa-new-field --named isbn
java-add-annotation --annotation org.hibernate.search.annotations.Field --on-property isbn
# create Book entity and relationship with Author
jpa-new-entity --named SellingPoint
jpa-new-field --named name
java-add-annotation --annotation org.hibernate.search.annotations.Indexed
java-add-annotation --annotation org.hibernate.search.annotations.Spatial
jpa-new-field --named latitude --type Double
jpa-new-field --named longitude --type Double
java-add-annotation --annotation org.hibernate.search.annotations.Longitude --on-property longitude
java-add-annotation --annotation org.hibernate.search.annotations.Latitude --on-property latitude
jpa-new-field --named books --type org.sellingPoint.model.Book --relationship-type Many-to-Many --fetch-type EAGER
java-add-annotation --annotation org.hibernate.search.annotations.IndexedEmbedded --on-property books
scaffold-generate --provider AngularJS --generate-rest-resources --targets org.sellingPoint.model.*
wildfly-swarm-detect-fractions --depend --build
# enable CORS
rest-new-cross-origin-resource-sharing-filter5.5. Add geospatial endpoint in SellingPoint
In src/main/java/org/sellingPoint/rest/SellingPointEndpoint.java add this method :
@GET
@Path("/inrange/{isbn}")
@Produces("application/json")
public List<SellingPoint> listByLocation(@PathParam("isbn") String isbn, @QueryParam("latitude") Double latitude,
@QueryParam("longitude") Double longitude) {
FullTextEntityManager fullTextEntityManager = Search.getFullTextEntityManager(em);
try {
fullTextEntityManager.createIndexer().startAndWait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
QueryBuilder builder = fullTextEntityManager.getSearchFactory().buildQueryBuilder()
.forEntity(SellingPoint.class).get();
org.apache.lucene.search.Query luceneQuery = builder
.spatial().within(5, Unit.KM).ofLatitude(latitude).andLongitude(longitude).createQuery();
org.apache.lucene.search.Query keyWordQuery = builder
.keyword().onField("books.isbn").matching(isbn).createQuery();
Query boolQuery = builder.bool().must(luceneQuery).must(keyWordQuery).createQuery();
javax.persistence.Query hibQuery = fullTextEntityManager.createFullTextQuery(boolQuery, SellingPoint.class);
return hibQuery.getResultList();
}5.6. Update Frontend App to consume the new SellingPoint Service
cp frontend_assets/sellingpoint/search.html bookstorefrontend/src/main/webapp/views/SellingPoint
cp frontend_assets/sellingpoint/searchSellingPointController.js bookstorefrontend/src/main/webapp/scripts/controllers
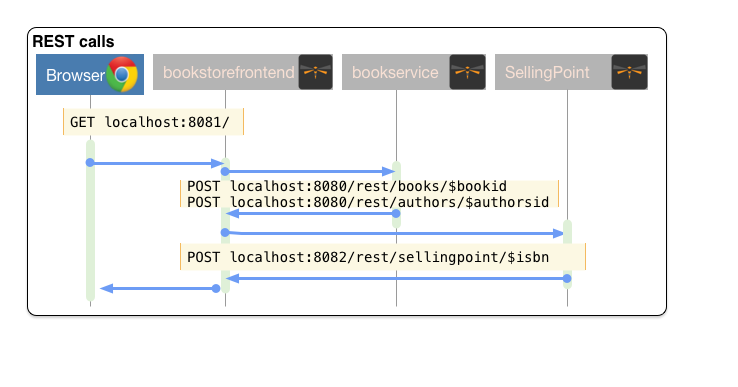
cp frontend_assets/sellingpoint/SellingPointFactory.js bookstorefrontend/src/main/webapp/scripts/servicesNow, from the http://localhost:8081/app.html#/SellingPoints you can search a specific Book by its isbn in a radius of 5 Km around you (your geolocation is automatically retrieved but you can override it on the search form).
To get back at least one result, make sure that your boostrap data contains at least a SellingPoint that is your area or use the SellingPoint embedded frontend http://localhost:8083/app.html.
5.7. Secure the endpoints with KeyCloak
5.7.1. Create Swarm Keycloak Server
project-new --named keycloakserver --stack JAVA_EE_7 --type wildfly-swarm --http-port 8083 --fractions keycloak-server5.7.2. Configure Keycloak Server
-
Browse to the keycloak console
localhost:8083/auth, you will have to create initially an Admin user -
Import
the demo realm -
This realm create a test user : username:
sebi/ password :password
5.7.3. Secure the services
(Be sure to start from the scripts folder)
# secure the bookService
cp bookservice_assets/keycloak.json bookservice/src/main/webapp/WEB-INF
cd bookservice
wildfly-swarm-add-fraction --fractions keycloak
security-add-login-config --auth-method KEYCLOAK --security-realm master
security-add-constraint --web-resource-name Book --url-patterns /rest/* --security-roles user
# The CORS filter is no longer needed, as KeyCloak will handle it from now
rm src/main/java/org/bookservice/rest/NewCrossOriginResourceSharingFilter.java
# redeploy and make sure the endpoint is protected by accessing directly its URL (i.e : localhost:8080/rest/books should show unauthorized)
cd ~~
cd ..
# Secure the frontend
cp frontend_assets/keycloak.json bookstorefrontend/src/main/webapp
cp frontend_assets/keycloak.js bookstorefrontend/src/main/webapp/scripts/vendor
cp frontend_assets/app.js bookstorefrontend/src/main/webapp/scripts
cp frontend_assets/app.html bookstorefrontend/src/main/webapp
cd bookstorefrontend
# Redeploy the frontend, it should now redirect to the keycloak login screen
cd ~~
cd ..
# secure the sellingPoint
cp sellingpoint_assets/keycloak.json sellingPoint/src/main/webapp/WEB-INF
cd sellingPoint
wildfly-swarm-add-fraction --fractions keycloak
security-add-login-config --auth-method KEYCLOAK --security-realm master
security-add-constraint --web-resource-name SellingPoint --url-patterns /rest/* --security-roles user
rm src/main/java/org/sellingPoint/rest/NewCrossOriginResourceSharingFilter.java
# SellingPoint is now secured.5.9. Putting it all together
You can run all the above commands from a single script. wsfk-hol.fsh
run wsfk-hol.fshLet’s generate the uberjar and run, using either ways:
mvn package && java -jar ./target/mylab-swarm.jaror
mvn wildfly-swarm:runor via your IDE with the Main class.
5.10. Bootstrap data
|
Important
|
For both of these scripts, make sure they have the name import.sql and put them in src/main/resources for each of the projects, they will be run at startup.
|
For the BookService :
insert into Author (id, name, version) values (1000,'Seb',0);
insert into Author (id, name, version) values (1001,'George',0);
insert into Book (id, title, isbn, author_id, version) values (1000,'Forge for Pro', '1001', 1000, 0);
insert into Book (id, title, isbn, author_id, version) values (1001,'Swarm for Pro', '1002', 1001, 0);For the SellingPoint Service :
insert into Book (id, isbn, version) values (1000, '1000',0);
insert into Book (id, isbn, version) values (1001, '1001',0);
insert into Book (id, isbn, version) values (1002, '1002',0);
insert into SellingPoint (id, latitude, longitude, name, version) values (2000, 43.5780, 7.0545, 'bob', 0);
insert into SellingPoint (id, latitude, longitude, name, version) values (2001, 43.574357, 7.1142449, 'chris',0);
insert into SellingPoint_Book (SellingPoint_id, books_id) values (2000,1000);
insert into SellingPoint_Book (SellingPoint_id, books_id) values (2000,1001);6. Extend the Demo with more capabilities
Now we have seen how to implement basic set of services, secure and monitor them, we would like to go one step further with moving those from traditional bare-metal environment to leverage new deployment model and targets. In the table below we explain briefly what capabilities are available in the different target environment to help you understand what you get for free or what you will to bring yourself depending on where you choose to deploy your services.
In this section we will demonstrate how to move the you build in the previous steps to Openshift and how you can benefit from its built-in capabilities.
| Capabilities | Bare Metal | Container | Openshift |
|---|---|---|---|
Management |
yes [Hawkular Fraction] |
yes |
yes |
Security |
yes [KeyCloak Fraction] |
yes |
yes |
Logging |
6.1. Polyglot microservices
In this section we will be taking some of our services and implementing them using Node.js, Vert.X and Spring Boot. We want them to be able to communicate with others services, remain secured and being monitored.
6.3. Deploying on Openshift
While this Lab has been focused on single machine/single instance development, there are critical capabilities that needs to be addressed if we want to deploy our solutions in productions. This section aims at listing those capabilities that comes for free in a PaaS environment like Openshift. We will demonstrate how our application can benefit from them.